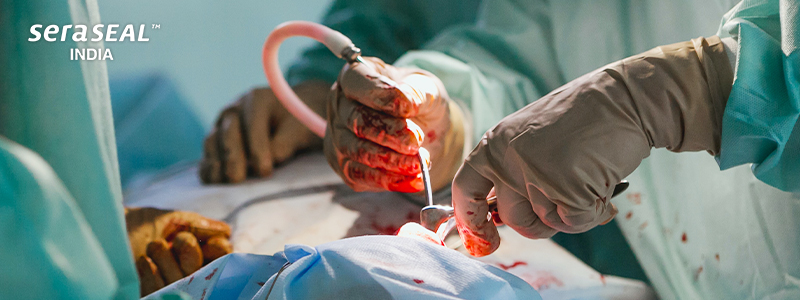
Death comes in different forms. One of them is excessive bleeding. Road accidents, extensive surgical procedures, violence, war, epidemics are the significant causes of loss of life due to hemorrhage.
Statistically speaking, epidemics killed 20-40 million people, and the world wars have caused around 55.9 million deaths. Out of which, 25% of the deaths were preventable and occurred due to blood loss. So it is high time we start doing something about the loss of life due to hemorrhage and uncontrolled bleeding.
War and road accidents are not the only causes of hemorrhage. Surgical procedures are often the cause of blood loss. Accidents happen on a surgery table as well. Hemorrhages are a common occurrence during surgery. Unfortunately, statistics describing the problem of controlling bleeding and using a hemostat are sparse.
#Did you know 7 million people worldwide suffer from surgical complications like excessive bleeding each year. 50% of these deaths are preventable.
You must’ve heard in the stories that, the doctor says, ‘the bleeding hasn’t stopped yet.’ But unfortunately, hemorrhages have a very high mortality rate, i.e., bleeding is significantly related to post-surgical deaths. So this raises the issue that bleeding has caused a substantial number of deaths, and how can we best prevent it?
We must first understand what causes bleeding during surgery to draft out the prevention methods.
What causes bleeding during surgery?
Various types of bleeding can occur during a surgical procedure. If the surgery is a success and not the cause for the bleeding, then we can say the bleeding is due to:
- Structural anomalies (anatomy)
- Recent drug intake
- Disorder od hemostasis
- Anticoagulant excess
- Hyperfibrinolysis
Among 25,048 procedures, major bleeding events occurred in 14,251 cases.
‘No blood loss’ is one aspect of a successful surgery. Surgical procedures have worked miracles with the help of technology. But hemorrhages always have been a threat. Controlling bleeding is the fundamental consideration in all surgeries. Advanced technology is required to control bleeding effectively. This would help minimize the adverse physiological sequelae of surgery, affecting patients’ recovery rate and increasing the need for transfusion. In addition, when there is no bleeding, it is easier to operate where the doctors can visibly see the organ. This would reduce the time taken for the surgery, avoid accidental injury to the patient, and decrease the chances of needle stick injury. Choosing the best pre-operative preparation for the patient, the best anesthetic support, and attentive surgical techniques are vital strategies for adequate hemostasis.
Yet, hemorrhages can still complicate a surgical procedure after preparations and effort. Therefore, a hemostatic agent is usually used to control the bleeding.
Major bleeding occurred in 32%–68% of cases despite treatment with hemostats.
The surgery will succeed if the patient does not suffer hemorrhage during or after the surgery. A practical, effective systematic, and topical approach can achieve hemostasis. A variety of hemostatic methods can be
employed, from applying pressure on the wound till cauterization, systematic administration of blood, or tropical application of pro coagulation agents.
The method level of bleeding experienced by the patient determines the surgical success. Therefore, the aim is to control and stop the bleeding. SeraSeal™ is the world’s first and only primary hemostatic agent. It STOPS THE BLEEDING IN SECONDS AFTER CONTACT Brought to India by Swasth Kare, SeraSeal™ is the ray of hope for the Indian medical fraternity.
Bottom Line
The chances of death may be a threat during a surgical procedure, but with the new technology, we have acquired the unstoppable SeraSeal™, a boon to medical innovation. It is a revolutionary hemostatic agent that stops bleeding in seconds, saving time, money, and effort. With SeraSeal™, the surgery is a success.
Contact us to know more about the world’s first and only primary hemostatic agent.